GENERAL ANAESTHESIA AND SEDATION
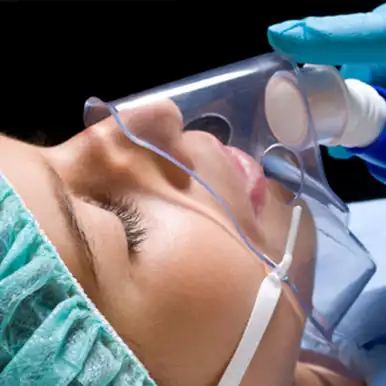
General anaesthesia is the type of anaesthesia in which a state of narcosis is provided by administering intravenous drugs and/or stun gas to the patient. Sedation, on the other hand, is anaesthesia which allows the patient make calm and relaxed, sometimes by administering sometimes intravenous drugs and sometimes oral drugs to the patient. The most important point here is to adjust the level of sedation. Considering that the treatment for which a sedation is applied will be performed in the mouth, there should be conscious sedation so that the patient's breathing is not compromised. Deep sedation can do more harm than good. For this reason, general anaesthesia is considered much safer than deep sedation. In addition, sedation does not have a numbing effect, so local anaesthesia is also applied to the patients in order to numb the area to be operated
WHO IS THE IDEAL CANDIDATE FOR GENERAL ANAESTHESIA / SEDATION IN DENTISTRY?
• In children with mental disabilities,
• In children with physical disabilities,
• In children or adults with whom no communication can be established despite the need for urgent treatment,
• In children at early age who have common caries called baby bottle caries or early childhood caries and cannot be treated with persuasion,
• In cases where medical risks (such as some systemic disorders) will decrease if general anaesthesia is used,
• For children, whose treatment should be completed in a single session for any reason (living in a far location, risk of allergic reaction, etc.),
• Adult patients with severe phobia (Fear)
• Patient group who want many surgical procedures that cannot be performed in a single session with local anaesthesia to be performed under general anaesthesia in a short period of time (like 2 hours).
DO I FEEL PAIN UNDER AND AFTER GENERAL ANAESTHESIA?
You will not feel any pain during the surgical procedure. In cases where tooth extraction is required, local anaesthesia is applied together with general anaesthesia. Only very young children may be disturbed by numbness arising due to local anaesthesia, which they are aware of after the surgery, or because of the sensation of gap in the area where the tooth extraction is made.
HOW LONG DO SURGICAL PROCEDURES PERFORMED UNDER GENERAL ANAESTHESIA TAKE?
IS IT NECESSARY TO STAY IN THE HOSPITAL AFTER GENERAL ANAESTHESIA?
The duration of the surgical procedure varies depending on the operations to be performed in the mouth of the patient. In this point, it should be noted that the dental treatment procedures do not start immediately as soon as the patient is taken to the operating room. The preparation phase of the patient can also take about half an hour in total before and after dental treatment procedures. After the procedure, patients are kept under supervision for approximately 1-2 hours and then discharged from the hospital.
THINGS TO CONSIDER BEFORE APPLICATION OF GENERAL ANAESTHESIA
• It is of great importance for our patients to fully inform their doctors about their current and past illnesses and the drugs used by them before general anaesthesia, and to comply with the dose adjustments of the drugs used by them before the surgery, in order to regain their health in the safest way during and after anaesthesia.
• Complications related to anaesthesia (general or sedation) are very rare, as long as it is performed in expert hands and under appropriate conditions. One of the most important things for anaesthesiologists is to make sure that you have not eaten anything prior to surgery. Because if the patient vomits under the full anaesthesia and this vomit passes into the lungs of the patient, it can lead to Lung Pneumonia (Pneumonia), which can be extremely severe and fatal. For this reason, we strongly want our adult patients to be at least 8 hours without food or water (such as fasting). In paediatric patients, it is important to pay attention to the hunger and thirst times that are told to you according to the age of the child.
• In order for the patient to be taken into general anaesthesia, the patient must not have any infection, such as a flu infection.