BRUXISM
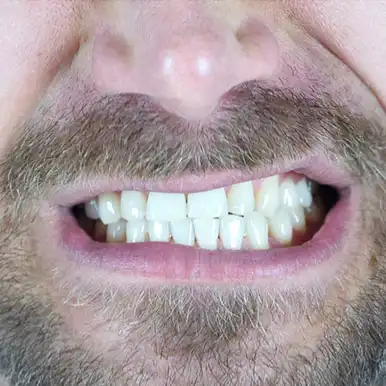
Bruxism is the involuntary rubbing of the upper and lower teeth against each other. It is commonly referred to as "teeth grinding" in daily use or among the public. It is more common in individuals with orthodontic tooth alignment disorders and malocclusions, and in children with allergy and asthma problems.
The most important reason for teeth grinding is orthodontic tooth misalignment and erroneous jaw closure, daily stresses, as well as diseases such as asthma and allergies at early ages.
If not treated, bruxism causes many problems such as abrasion of dental hard tissues, fracture of teeth, hypersensitivity, problems in gingival tissues (such as gingival recession), sagging teeth, pain in the head and neck region, problems in the temporomandibular joint, limited mouth opening and closing, and jaw locking.